- This topic is empty.
-
AuthorPosts
-
2025-07-09 at 1:50 pm #9941
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, welding positioners have emerged as game-changing equipment that fundamentally transforms argon arc welding (TIG welding) operations. As a cornerstone process for metal fabrication, welding quality and throughput directly impact product integrity and production economics. TIG welding machines, renowned for their precision in handling diverse metals, low thermal distortion, and exceptional weld purity, have become indispensable in aerospace engineering, automotive manufacturing, and shipbuilding industries. The strategic implementation of industrial welding positioners now represents a crucial advancement in achieving superior weld consistency and operational efficiency.
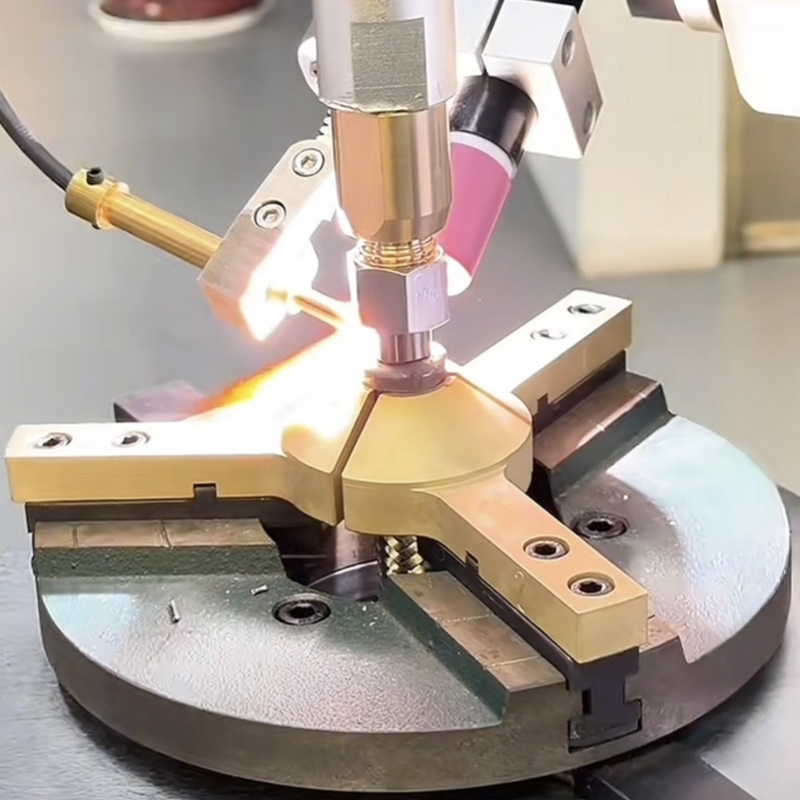
The synergy between TIG welding technology and automated positioning systems stems from argon's unique protective properties. During the welding process, inert argon gas forms a protective shield around the weld pool, effectively preventing oxidation and contamination from atmospheric elements. This characteristic makes gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) particularly effective for oxidation-sensitive materials like stainless steel, aluminum alloys, and titanium alloys. However, traditional fixed-position welding methods struggle with complex geometries and variable joint orientations, creating demand for advanced welding positioner solutions.
Modern welding positioner equipment addresses these challenges through precision articulation capabilities. Heavy-duty welding rotators and programmable tilt-rotate systems enable optimal positioning of weld joints through controlled rotation, inversion, and angular adjustment. By maintaining the ideal flat welding position (1G position), these systems ensure proper molten metal flow under gravitational forces, significantly reducing defects like incomplete fusion or excessive reinforcement. Consider the fabrication of large pressure vessels: manual welding without positioners requires constant repositioning, leading to inconsistent quality. Implementing a motorized welding turntable allows continuous rotation, maintaining the weld seam in the optimal horizontal position while operators work from fixed stations.
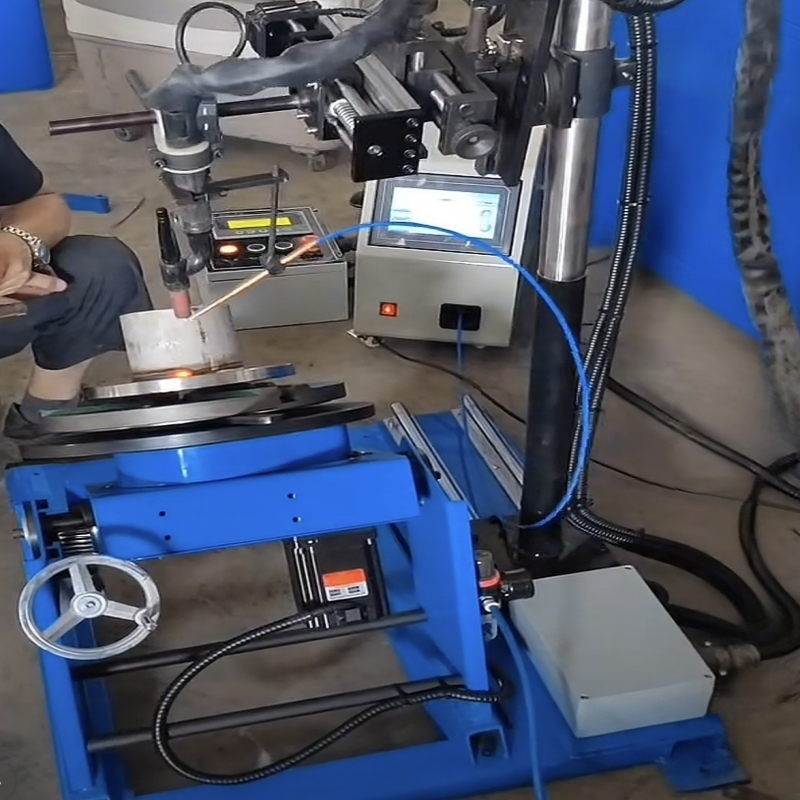

The integration of CNC-controlled welding positioners with TIG welding power sources elevates automation to unprecedented levels. Sophoticated servo-driven positioners synchronize with pulsed TIG welding parameters through PLC interfaces, enabling:
1. Automated weld seam tracking with laser guidance systems
2. Precision speed coordination between workpiece rotation and torch movement
3. Adaptive current/voltage adjustments for complex joint configurations
4. Repeatable positioning accuracy (±0.1° typical for aerospace-grade systems)
This welding automation technology dramatically reduces human error while increasing throughput by 40-60% in typical applications. Manufacturers report 30% reductions in post-weld rework when implementing robotic welding positioners with integrated arc sensing capabilities.
Diverse welding positioner configurations cater to specific industrial requirements:
– Single-axis motorized turntables: Ideal for pipe welding and circumferential joints
– Dual-axis headstock-tailstock systems: Enable compound angles for structural components
– H-frame inverter positioners: Facilitate 180° flipping for double-sided welding
– Customizable 3D servo positioners: Accommodate complex aerospace components
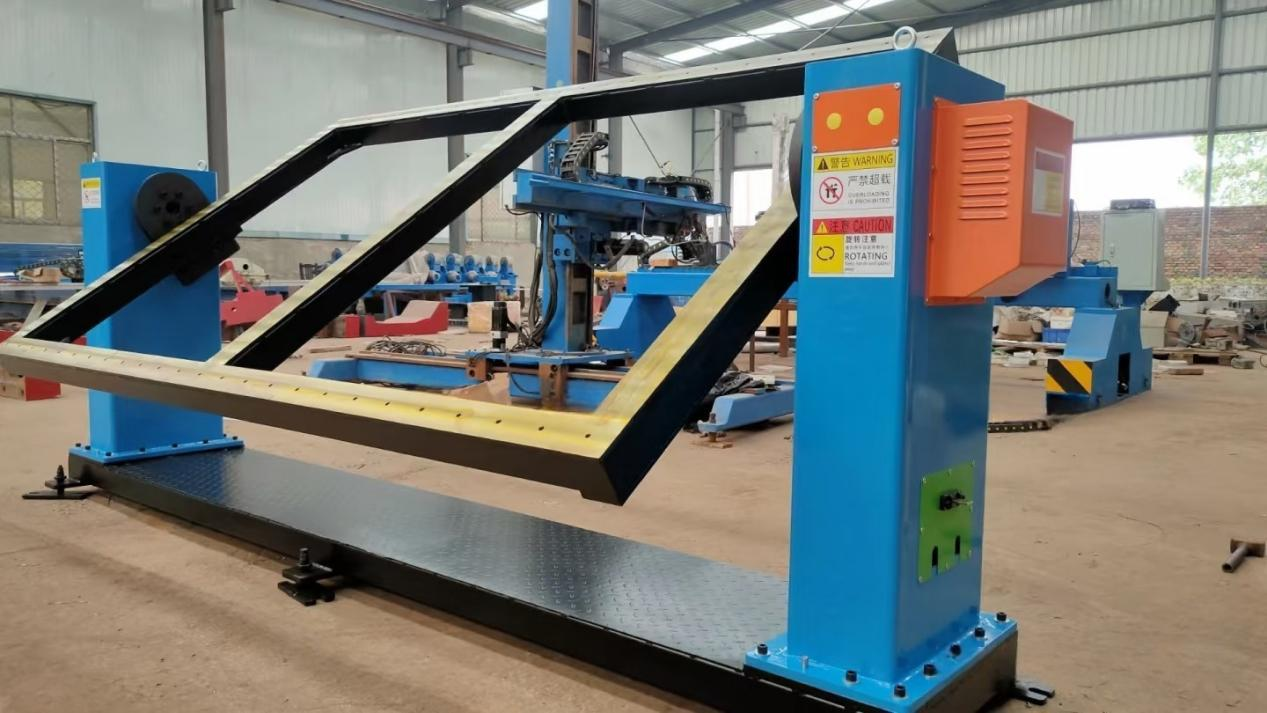

When selecting welding positioning equipment, manufacturers must consider:
1. Load capacity (standard models handle 500kg-20ton payloads)
2. Rotation speed ranges (0.1-2.5 RPM typical)
3. Control system compatibility (EtherCAT, Profibus, etc.)
4. Safety certifications (CE, ISO 10218 for collaborative robotics)
Critical implementation factors include:
– Precision alignment between positioner axis and weld joint geometry
– Proper shielding gas coverage during dynamic movement
– Thermal management for high-duty-cycle operations
– Regular maintenance of rotary unions and slip rings
Recent advancements in smart welding positioners incorporate:
– AI-powered adaptive welding algorithms
– Real-time weld quality monitoring via vision systems
– IoT-enabled predictive maintenance features
– HMI interfaces with 3D simulation capabilities
The strategic deployment of welding positioner technology in TIG welding operations delivers measurable benefits:
1. 75% reduction in positional welding defects
2. 50% decrease in operator fatigue
3. 3:1 ROI through reduced cycle times and material savings
4. Improved compliance with ASME Section IX and AWS D1.1 standards
As Industry 4.0 transforms manufacturing, next-generation welding positioners with 5G connectivity and digital twin integration are setting new benchmarks for precision joining technologies. From automated orbital welding systems for pipeline construction to robotic welding cells with adaptive fixturing, these advanced positioning solutions continue redefining quality standards in critical welding applications.
If you have any welding machinery needs, please contact us through Resize Welding Machinery Web: www. resizeglobal.com
http://www.resizeglobal.com
Resize welding machinery -
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.
